10x Genomics
Chromium Single Cell Gene Expression
Cell Ranger7.1 (latest), printed on 07/07/2025
The Cell Ranger User Interface
Cellranger's pipelines expose a user interface (UI) for monitoring progress
through a web browser. By default, this UI is exposed at an operating-system
assigned port, with a randomly-generated authentication token to restrict
access. Specifying the --uiport=3600 option when using
cellranger will force the UI to be exposed on port 3600, and the
--disable-ui option will turn off the UI.
This UI is accessible through a web interface that runs on the given port on
the machine where the pipeline was started. The URL to use with the web
browser is printed to the pipeline standard output and log files, and can
also be found in the [sampleid]/_uiport file where the pipeline
was launched.
Understanding the UI
When the pipeline runs, it will display the URL for the UI.
$ cellranger count --id=sample345 \ --transcriptome=/opt/refdata-gex-GRCh38-2020-A \ --fastqs=/home/jdoe/runs/HAWT7ADXX/outs/fastq_path \ --indices=SI-3A-A1 \ --expect-cells=1000 \ Martian Runtime - v4.0.8 Serving UI at http://host.example.com:5603/?auth=mcV3MKANWfNTERRGASgYV8aXskx-rSH7hxynAdsTieA 2012-01-01 12:00:00 [runtime] Reattaching in local mode. Running preflight checks (please wait)...
The UI will become unavailable once the pipeline completes unless the
--noexit flag is passed.
While a pipeline is running, you can open the url ( http://host.example.com:5603/?auth=mcV3MKANWfNTERRGASgYV8aXskx-rSH7hxynAdsTieA) in your web browser to view the pipeline process graph:
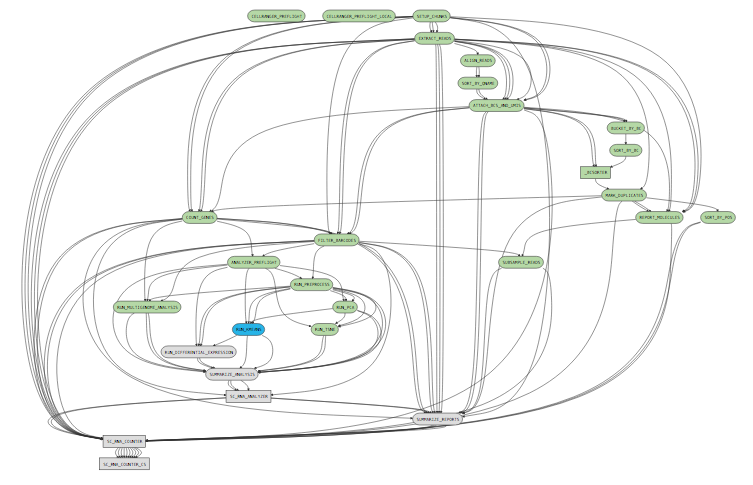
Clicking on any of the graph's nodes will reveal more information about that stage in the right pane. This info pane is broken into several sections, and the topmost shows high-level details about the stage's execution. For example, the RUN_KMEANS stage would show:
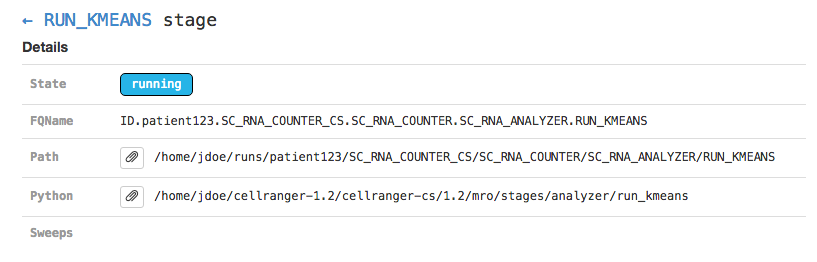
This includes the state of the stage (running, failed, or complete), the fully-qualified stage name (FQName), the directory in which the stage is running (Path), the stagecode that is being run (the location of the Python package being run in the above example), and any information about parameter sweeping that may apply to this stage.
Clicking the arrow next to the stage name (← RUN_KMEANS in the above example) will return to the pipeline-level metadata view.
The Sweeping section allows you to view the MRO call used to invoke this stage (invocation) and information about the split and join components of the stage if it was parallelized.
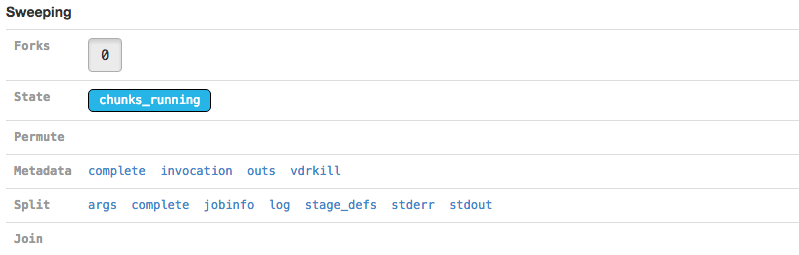
| Martian, the pipeline framework used by Cell Ranger, supports parameter sweeping for pipelines. The Forks and Permute fields in the Sweeping section would display information about different parameters being swept, but no Cell Ranger pipeline currently performs parameter sweeping. These fields will always contain only trivial information as a result. |
The Argument Bindings and Return Bindings sections display the inputs and outputs of the stage:
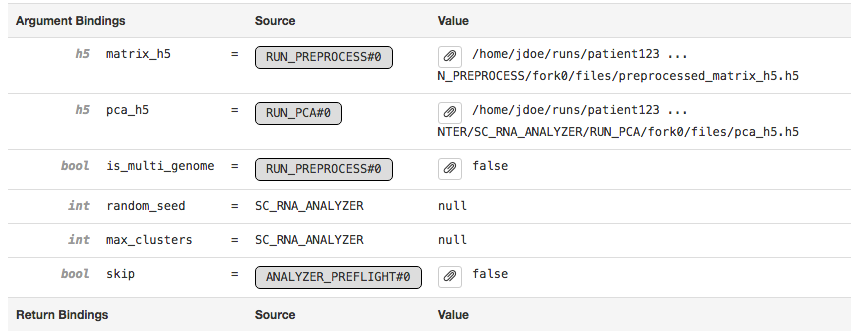
In general, only top-level pipeline stages (those represented by rectangular nodes in the process graph) contain return bindings.
The Chunking section displays information about the parallel execution of the stage:
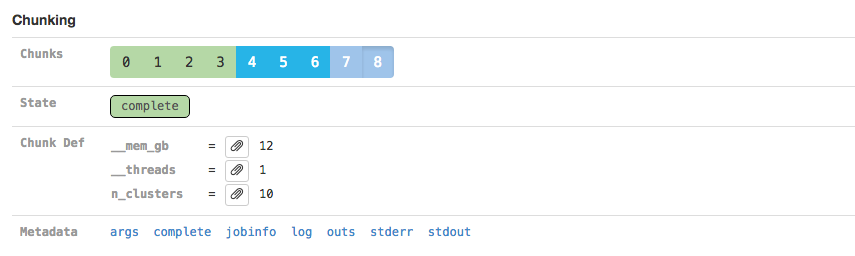
Many stages are automatically parallelized and process different pieces (chunks) of the same input dataset in parallel. In the above example, the input dataset (the BAM file from the SORT_BY_BC stage according to the Argument Bindings section above) was split into 39 chunks for this stage. Chunks 0-30 already completed, 31-35 are in flight, and 36-38 are waiting for CPU and/or memory to become available before running.
Clicking on an individual chunk exposes additional options for viewing metadata about that chunk's execution, including any errors, standard output, and in cluster mode the job script used to queue the job to the cluster. The jobinfo includes information about how a chunk was executed, selected environment variables, and for completed chunks various perfomance statistics such as peak memory usage and CPU time used. As with the Sweeping section, additional metadata associated with the chunk execution can also be viewed.
Launching the UI for existing pipelines
You can also examine pipestances that have already completed using the
Cell Ranger UI. Assuming your pipestance output directory was
/home/jdoe/runs/sample345, simply re-run the cellranger
command with the --noexit option to re-attach the UI:
$ cellranger count --id=sample345 \ --transcriptome=/opt/refdata-gex-GRCh38-2020-A \ --fastqs=/home/jdoe/runs/HAWT7ADXX/outs/fastq_path \ --indices=SI-3A-A1 \ --expect-cells=1000 \ --noexit Martian Runtime - v4.0.8 Serving UI at http://host.example.com:3600 2012-01-01 12:00:00 [runtime] Reattaching in local mode. Running preflight checks (please wait)... Pipestance completed successfully, staying alive because --noexit given.
Because cellranger assumes it is resuming an incomplete pipeline job when re-attaching, the pipeline must be valid and preflight checks must still be passed. As such, relocating a complete pipeline may prevent the UI from re-attaching.
Accessing the UI through a firewall
If you run pipelines on a server that blocks access to all ports except SSH, you can still access the Cell Ranger UI using SSH forwarding. Assuming you have a cellranger pipeline running on port 3600 on cluster.university.edu, you can type the following from your laptop:
$ ssh -NT -L 9000:cluster.university.edu:3600 jdoe@cluster.university.edu jdoe@cluster.university.edu's password:
Upon entering your password (assuming you are jdoe@cluster.university.edu), the command will appear to hang. However, in the background it has mapped port 9000 on your laptop to port 3600 on cluster.university.edu through the ssh connection for which you just entered your password.
This allows you to go to http://localhost:9000/ in your web browser and access the UI running on cluster.university.edu:3600. Once you are done examining the UI, use Ctrl+C in your ssh -NT -L ... terminal window to terminate this SSH forwarder.
A full explanation of SSH forwarding is beyond the scope of this guide, please see SSH/OpenSSH/PortForwarding.