10x Genomics
Chromium Single Cell ATAC
Cell Ranger ATAC1.2, printed on 08/13/2025
What is Cell Ranger ATAC?
Cell Ranger ATAC is a set of analysis pipelines that process Chromium Single Cell ATAC data. Cell Ranger ATAC includes four pipelines relevant to single cell chromatin accessibility experiments:
-
cellranger-atac mkfastq demultiplexes raw base call (BCL) files generated by Illumina® sequencers into FASTQ files. It is a wrapper around bcl2fastq from Illumina®, with additional useful features that are specific to 10x Genomics libraries and a simplified sample sheet format.
-
cellranger-atac count takes FASTQ files from cellranger-atac mkfastq and performs ATAC analysis, including:
- Read filtering and alignment
- Barcode counting
- Identification of transposase cut sites
- Detection of accessible chromatin peaks
- Cell calling
- Count matrix generation for peaks and transcription factors
- Dimensionality reduction
- Cell clustering
- Cluster differential accessibility
-
cellranger-atac aggr aggregates and analyzes the outputs from multiple runs of cellranger-atac count (such as from multiple samples from one experiment) by performing the following steps:
- Normalization of input runs to same median fragments per cell (sensitivity)
- Detection of accessible chromatin peaks
- Count matrix generation for peaks and transcription factors for the aggregate data
- Dimensionality reduction
- Cell clustering
- Cluster differential accessibility
-
cellranger-atac reanalyze takes the analysis files produced by cellranger-atac count or cellranger-atac aggr and reruns secondary analysis with tunable parameter settings:
- Cell calling
- Dimensionality reduction
- Cell clustering
- Cluster differential accessibility
Output is delivered in standard BAM, MEX, CSV, TSV, HDF5 and HTML formats that are augmented with cellular information.
The count pipeline can take input from multiple sequencing runs on the same library.
Chemistry
Cell Ranger ATAC 1.0, 1.1 and 1.2 support libraries generated by the Chromium Single Cell ATAC v1 reagent kits.
Workflows
10x Genomics recommends using the pipeline analysis programs in order, starting with cellranger-atac mkfastq for demultiplexing the raw base call (BCL) files for each flowcell directory, and continuing with cellranger-atac count for single library analysis. If compatible FASTQ files are available from another source, a user can skip cellranger-atac mkfastq and use those FASTQ files as direct input to cellranger-atac count. Compatible FASTQ files can be found in reputable public datasets, or can be built by using bcl2fastq directly. See the Specifying Input FASTQs page for more details
The subsequent steps vary depending on how many samples, GEM wells, and flowcells you have (see the Glossary of Terms for detailed definitions). The relationship between these terms can be complex as there are multiple ways samples can be prepared for the pipeline. They are described here in order of increasing complexity. Note that the term library and GEM well are treated as equivalent because a single library (for Single Cell ATAC v1) is associated with data from one GEM well in the 10x Genomics Chromium Controller run.
One Sample, One GEM Well, One Flowcell
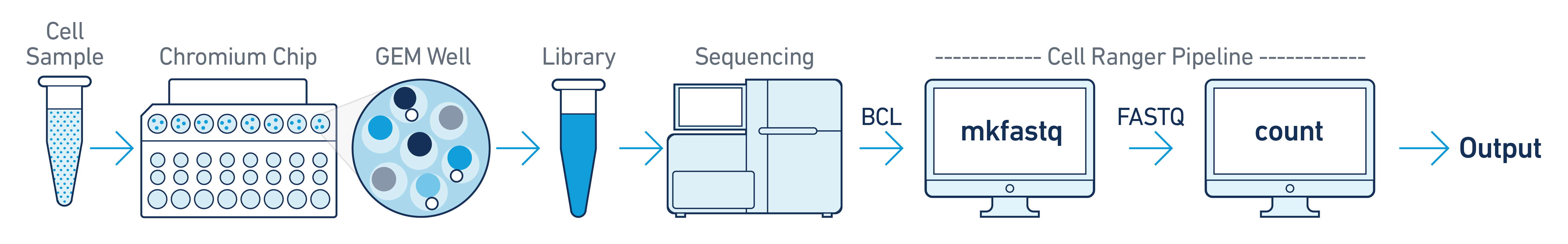
This is the most basic case. You have a single biological sample, which was prepared into a single library by processing through one GEM well (a set of partitioned cells from a single 10x Chromium™ Chip channel), and then sequenced on a single flowcell. Assuming the FASTQs have been generated with cellranger-atac mkfastq, you just need to run cellranger-atac count as described in Single-Library Analysis.
One Sample, One GEM well, Multiple Flowcells
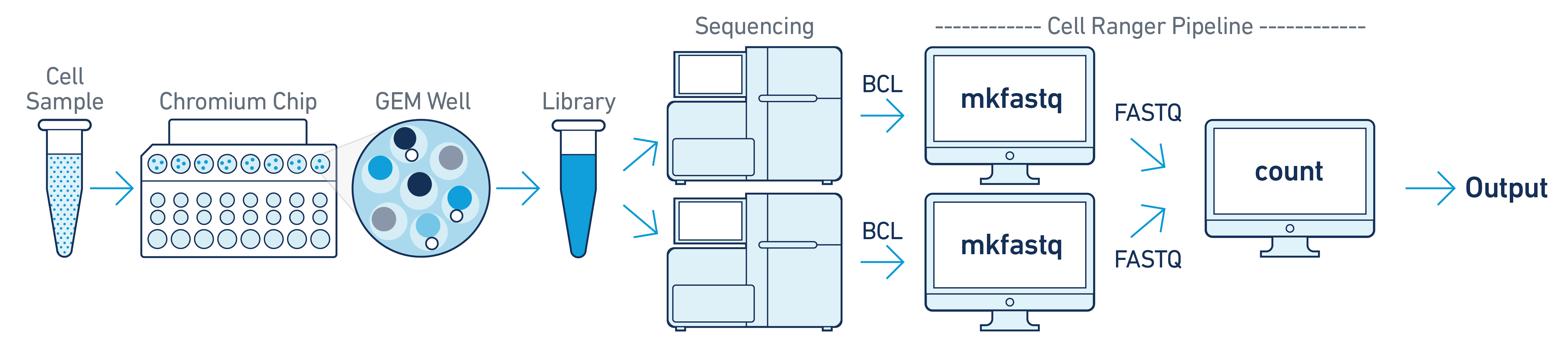
If you have a library generated from a single GEM well but was sequenced across multiple flowcells (e.g. to increase sequencing saturation), you can pool the reads from both sequencing runs. Follow the steps in Specifying Input Fastqs to combine them in a single cellranger-atac count run.
One Sample, Multiple GEM Wells, One Flowcell
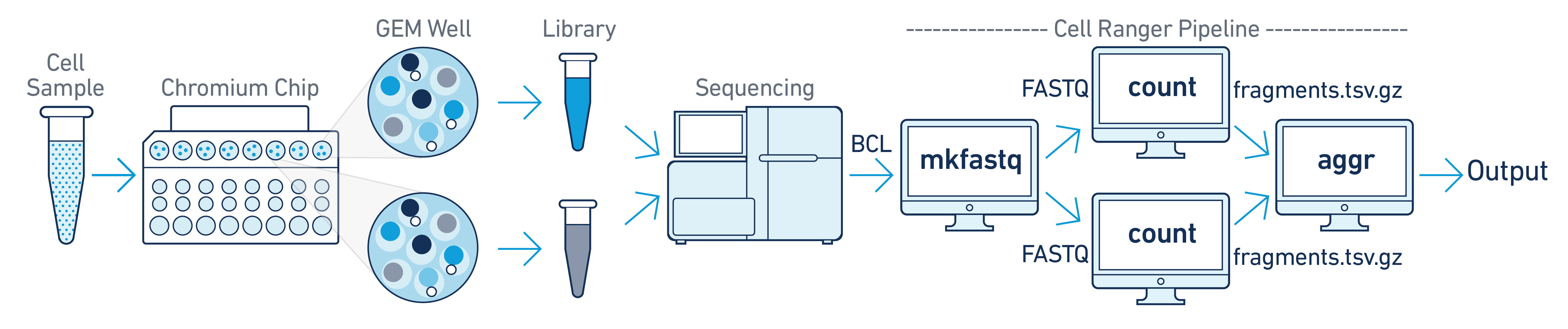
In this example you have one sample that is processed through multiple GEM wells. This is often done when conducting technical replicate experiments, or to increase the number of cells in your library without overloading a single GEM well in a 10x Genomics Chromium Controller run. The libraries from the GEM wells are then pooled onto one flowcell and sequenced. In this case you demultiplex the data from the sequencing run and then run the libraries from each GEM well through a separate instance of cellranger-atac count. Once those are completed, you can perform a combined analysis using cellranger-atac aggr, as described in Multi-Library Aggregation. (See figure above.).
Multiple Samples, Multiple GEM Wells, One Flowcell
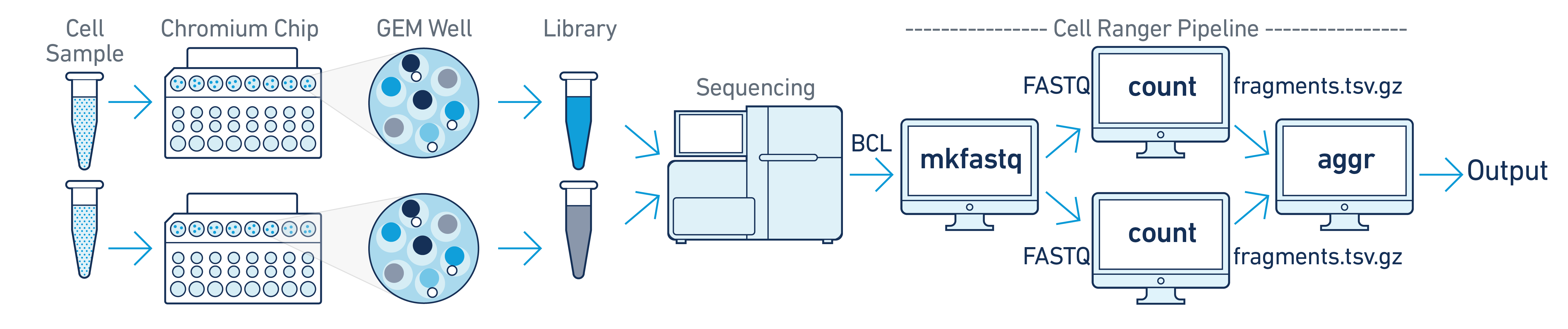
In this example you have multiple samples that are processed through multiple GEM wells which generate multiple libraries and are pooled onto one flowcell. In this case, after demultiplexing, you must run cellranger-atac count separately for each GEM well to get sample specific data. For example, if your experimental design involves two samples, you will have to run cellranger-atac count two times - once for each sample. Then you can aggregate them with a single instance of cellranger-atac aggr, as described in Multi-Library Aggregation.
- 2.1 (latest)
- 2.0
- 1.1
- 1.0
- Cell Ranger ATAC v1.2